Last updated May 30, 2024
Introduction
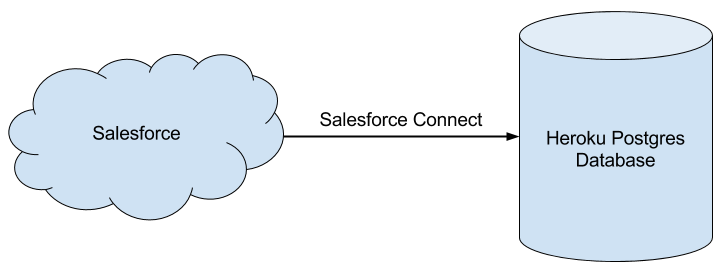
This guide shows how to use Heroku External Objects and Salesforce Connect to integrate data from a Heroku Postgres database into Salesforce. All of this is done by reference: the data remains in Heroku Postgres, but it can be read from and, in most cases, written to from within Salesforce.
Heroku External Objects works with Heroku Connect enterprise and shield plans. demo plans are unsupported.
The PostgreSQL data that we are using is from a sample DVD rental database. See the Appendix section for instructions on how to import the data into a Heroku Postgres database.
Salesforce Connect is a separate product from Heroku Connect. If you don’t already have Salesforce Connect, contact Salesforce for licensing information.
Setting up Heroku External Objects
As a prerequisite, you must provision the Heroku Connect add-on. Using Heroku Connect to sync data with Salesforce is optional: if you’re only interested in Heroku External Objects, you can skip the step that asks you to authorize your connection with Salesforce.
You’ll see an External Objects tab on your Heroku Connect dashboard:

If it’s your first time using Heroku External Objects, you’re prompted to create the OData service’s login credentials. After you’ve completed this step, you can view and manage the login credentials at any time from the dashboard.
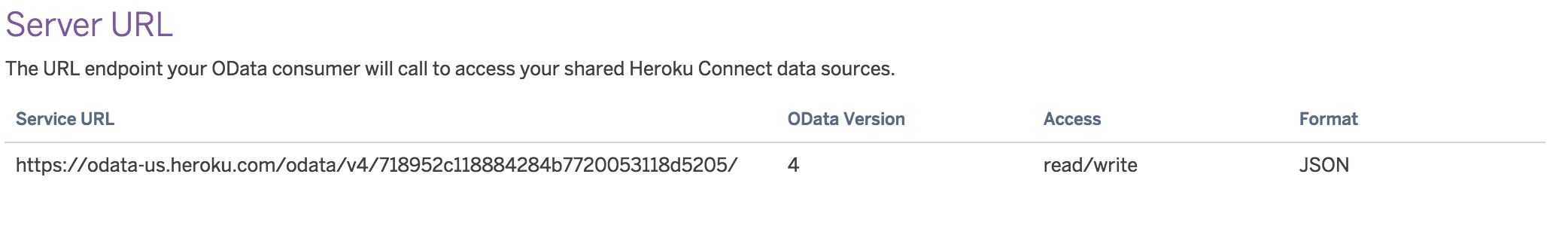
Note the OData 4.0 service URL:
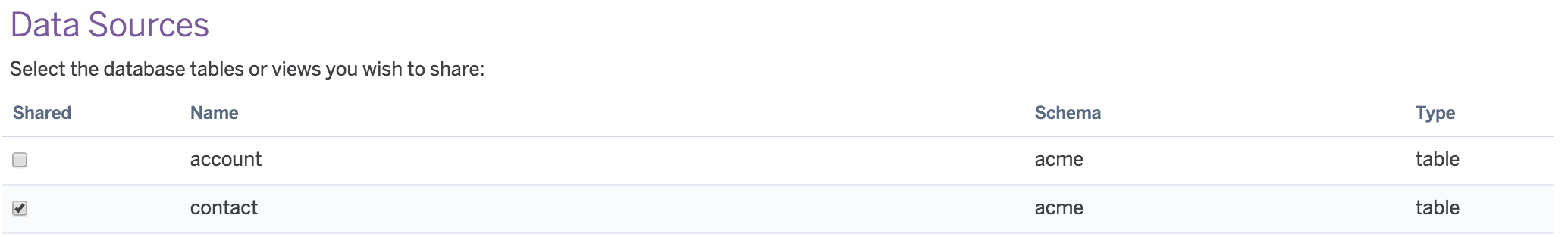
To complete the setup, you must choose the tables and/or views to expose. All schema within your Heroku Postgres database is available, including those schema not actively managed by Heroku Connect.
Unlike tables, views don’t currently support writes. Additionally, Connect requires that each view contain a uniquely valued column named ‘id’.
Using Salesforce Connect
Now we can set up the OData service as an External Data Source in your Salesforce org. In the Salesforce setup menu, type “External” into the quick find box and choose “External Data Sources”. The interface for creating a new external data source looks like this:
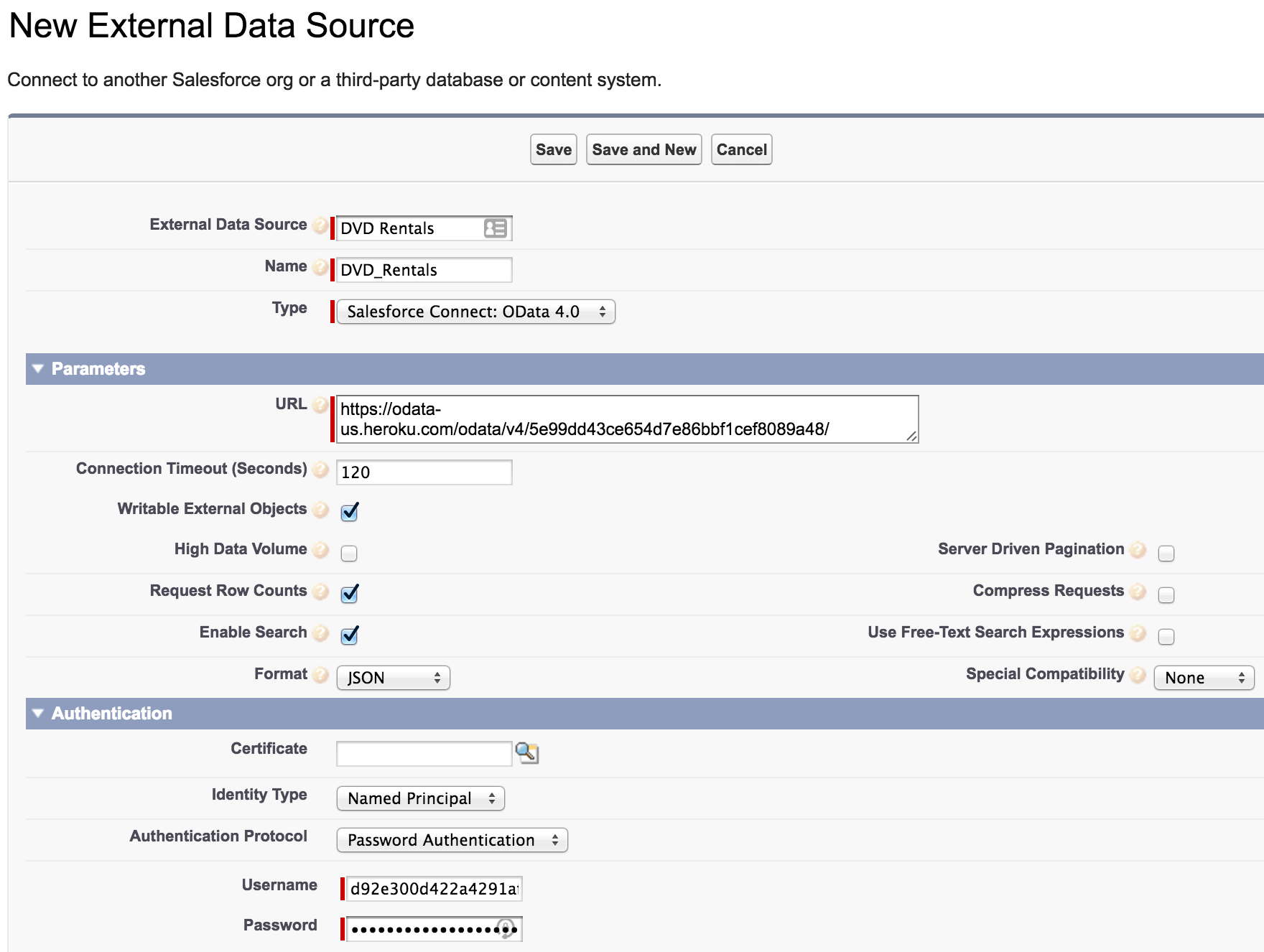
Be sure to select Writable External Objects if you’d like to use the read/write capabilities of OData 4.0.
Since we use a single password, choose “Named Principal” as the Identity Type and “Password Authentication” as the Authentication Protocol. Your username and password are available from the Heroku External Objects dashboard. If you reset your Heroku External Objects credentials, you must also update the username and password in your Salesforce setup.
After saving your External Data Source, click Validate and Sync to check the connection and synchronize its schema.
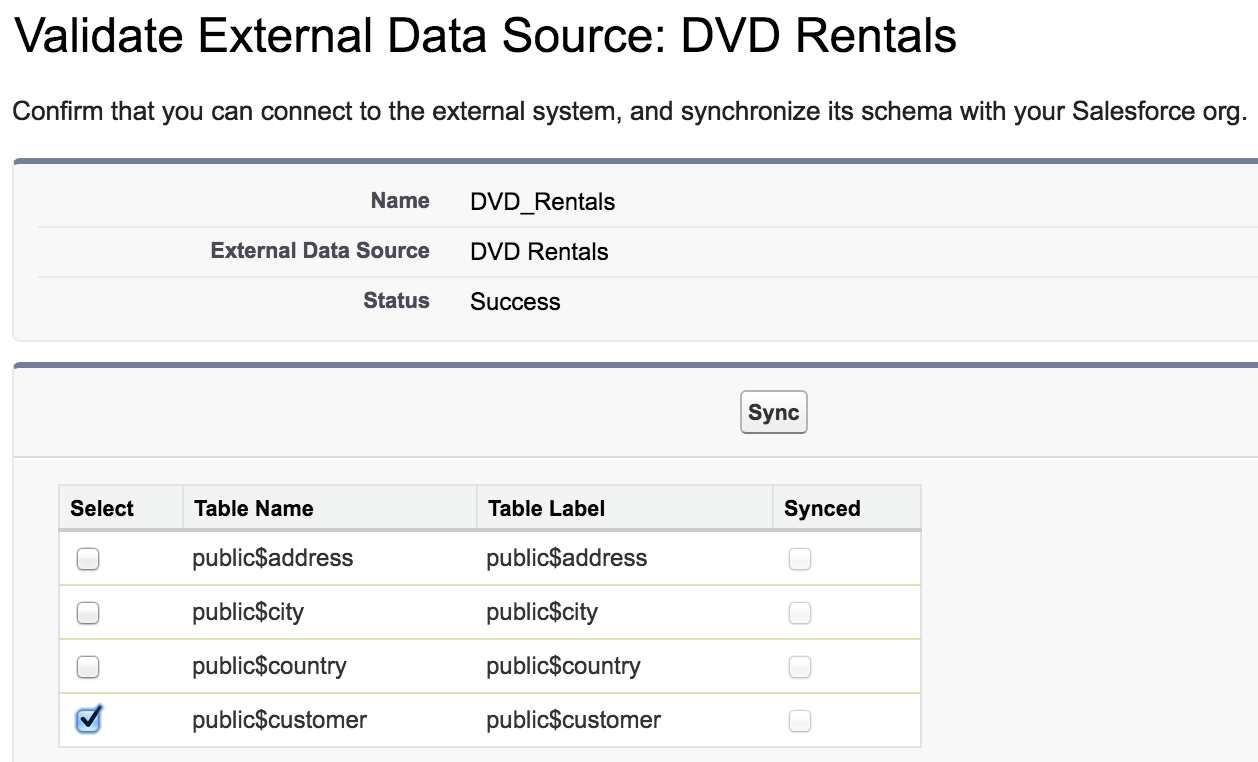
Each table you select is an External Object. Initially their names have $ characters instead of periods, but you can edit the labels.

We can call ours “External Customer”.
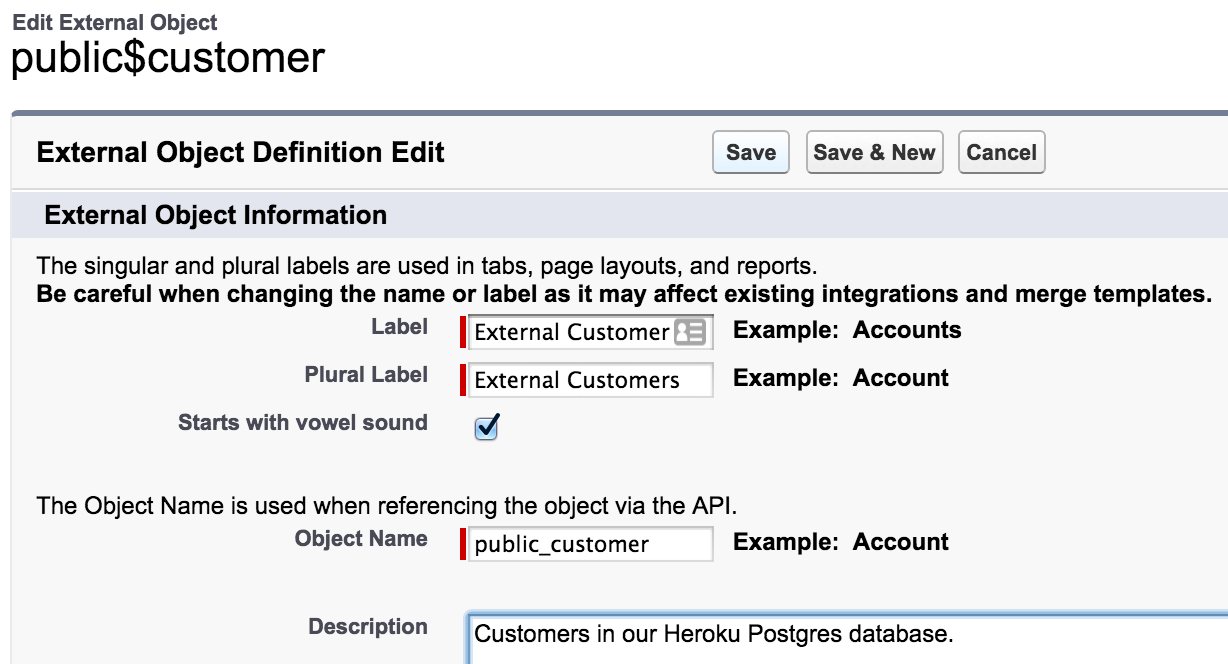
Like any other object, you can create custom object tabs and customize layouts for External Objects.
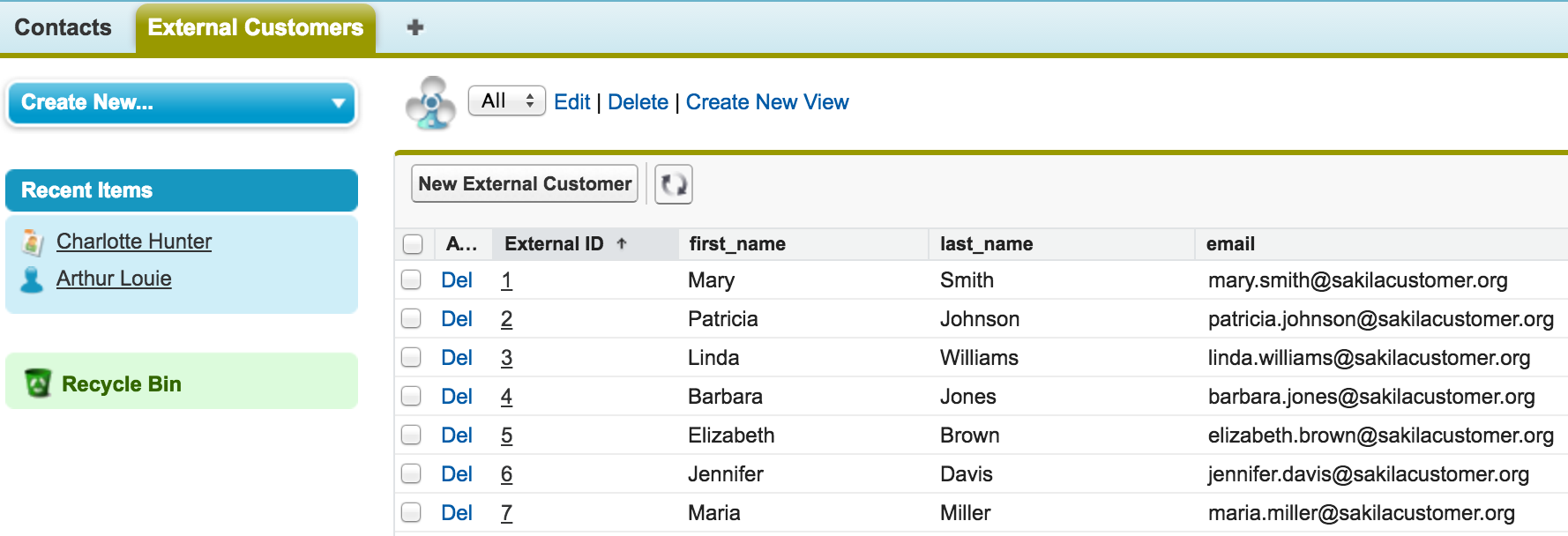
We can also make SOQL queries against our external object, which has the API name public_customer__x.
SELECT Contact__c, first_name__c, last_name__c FROM public_customer__x
And since we enabled writes, any create/update/delete operations are written to the Heroku Postgres database.
Using External IDs to Relate External Objects
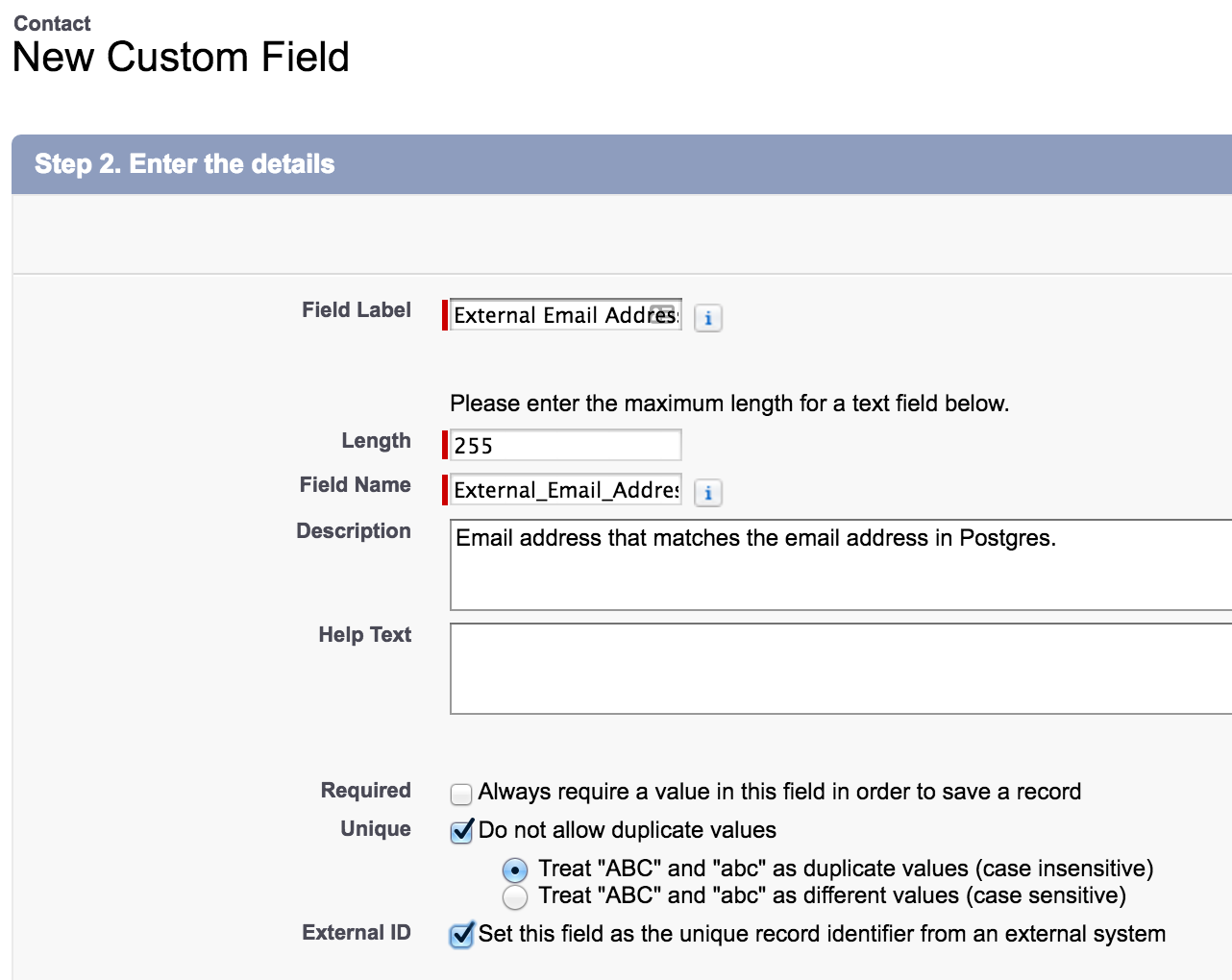
We can also use external IDs to associate records in Salesforce with their corresponding records in Postgres. Let’s create an external ID field on Salesforce contact objects, which links the records using the customer’s email address.
Create a new custom field on Contact and select String as the type. The value of the field is the customer’s email address, and it must be defined as a unique external ID:
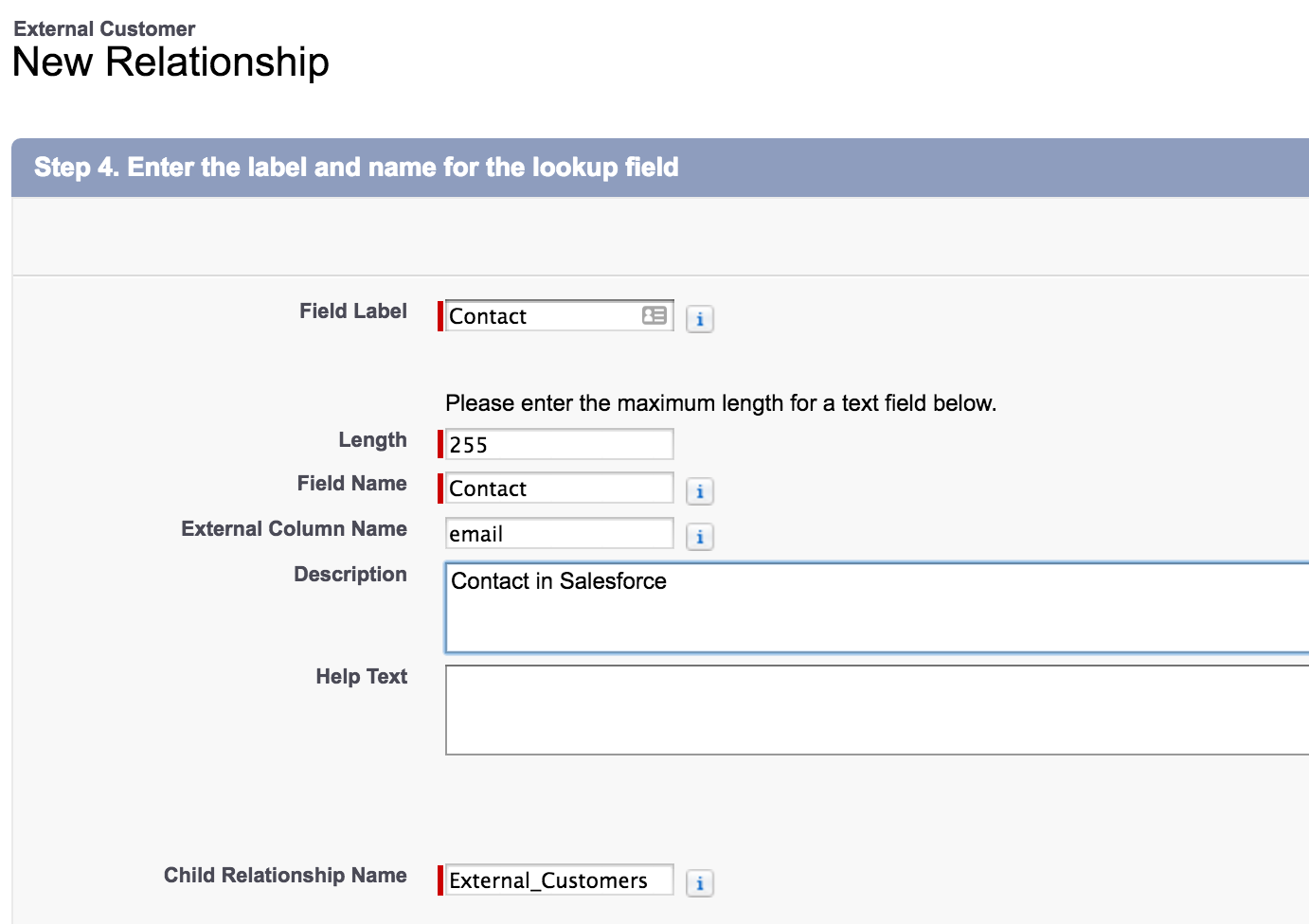
Now we can add an indirect lookup relationship on the external object:

On the next screens, relate it to the Contact object (Step 2) and choose the external ID field (Step 3).
In Step 4, be sure to specify email as the external column name.
We’re done – contacts in Salesforce with External Email Address fields are now related to their External Customer records. Clicking the email address link on this External Customer record takes us to Mary’s contact record in Salesforce.
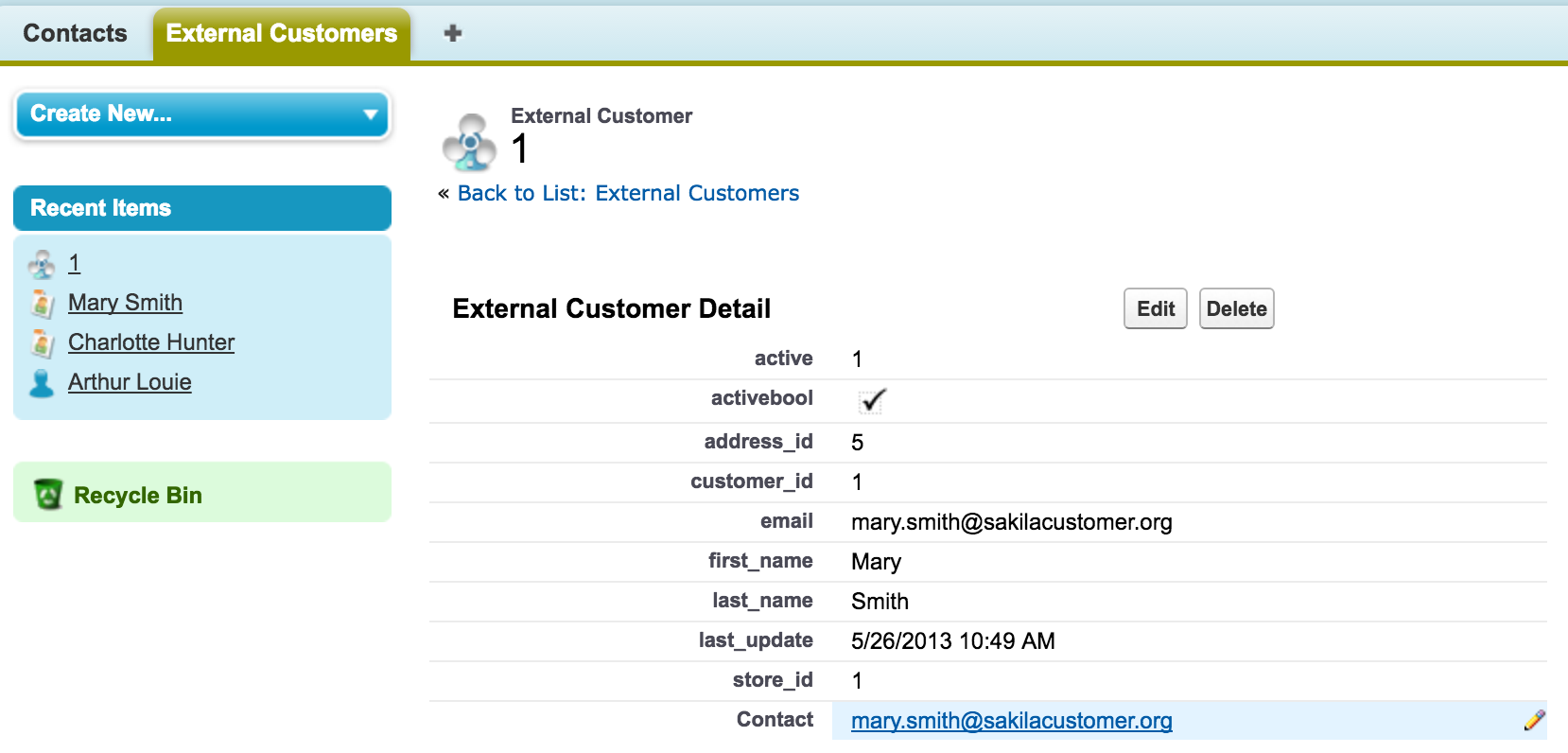
Mary’s contact record also has a related list that links back to the external object.

Resetting Your Credentials
When you reset your Heroku External Objects credentials, your old credentials are still available for 10 minutes so that you can update your integrations without incurring downtime.
To reset your Heroku External Objects credentials, do the following:
Locate your connection in the Heroku Connect dashboard, and click the External Objects tab.
Click “Reset credentials”.
Click “Yes” when prompted to reset the credentials.
Assuming that you have External Objects defined in Salesforce, edit your existing OData 4.0 External Data Source in Salesforce to use the new credentials.
References
- Salesforce Connect documentation
- OData 2.0 and 4.0 Adapter documentation
- Salesforce Connect Trailhead module
Appendix: Importing Sample Data
Importing the data from the sample DVD rental database to Heroku Postgres requires you to:
- Download and extract the sample database
- Import the database to your local PostgresSQL server
- Export the database to a dump file
- Import the database dump to Heroku Postgres
It’s not possible to import the dvdrental.tar file directly to Heroku Postgres because it’s not in the format the Heroku Postgres requires.