Table of Contents [expand]
Last updated December 03, 2024
Heroku’s Logplex router is responsible for collating and distributing the log entries generated by your app and other components of the Heroku platform. It makes these entries available through the Logplex API and the Heroku command-line tool.
In a distributed system such as Heroku, manually accessing logs spread across many dynos provides a disjointed view of an application’s event stream and omits relevant platform-level events. The Logplex facility solves these issues in an accessible and extensible manner.
Shield spaces with Private Space Logging enabled and Fir-generation apps do not use Logplex. See Private Space Logging and Heroku Telemetry for Fir for more info.
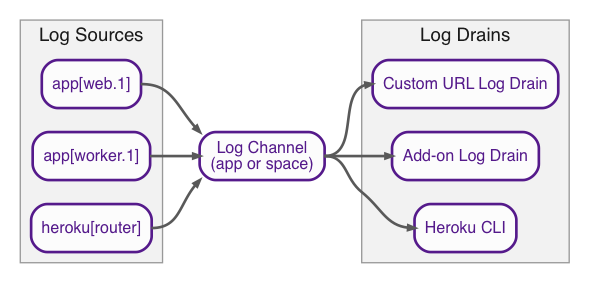
Sources and drains
Logplex routes messages from sources to drains.
Log sources are any processes that want to emit log entries relevant to your app. Some examples: your
webdynos, the Heroku platform, the Heroku routing stack, and many add-ons.Log drains are any network services that want to consume your app’s logs, either for automatic processing, archival, or human consumption. Examples include the Heroku command-line tool and several log-processing and management add-ons.
Best-effort delivery
Logplex is a high-performance, real-time system for log delivery – not storage. It keeps a limited buffer of log entries.
Logplex interacts directly with various external tools and services, and requires prompt action for real-time processing. If one of these services has trouble keeping up, Logplex can be forced to discard log entries for some time. If this happens, it inserts a warning entry to indicate that some entries are missing.
Logplex residency
Logs for the Common Runtime are routed in the same region the app is running within. For example, logs for an app in the us region gets routed through the us infrastructure.
Logs for apps in Private Spaces stay within the same region as the space itself. For example, logs for an app in a Tokyo space routes through the infrastructure in Tokyo.
You can deploy apps with strict compliance requirements in Shield Private Spaces, which uses Private Space Logging to route logs instead of Logplex.
See the Salesforce Infrastructure & Sub-processors document for the list of sub-processors Heroku uses and the list of countries where Heroku data is stored and processed.